Major Arteries In Neck / Cardiovascular System of the Head and Neck
Major Arteries In Neck / Cardiovascular System of the Head and Neck. Major aortopulmonary collateral arteries (mapcas) are persistent tortuous fetal arteries that arise from the descending aorta and supply blood to pulmonary arteries in the lungs usually at the posterior aspect of hilum. Yes the blood pressure in major arteries in the leg is greater than the blood pressure in arteries in neck during orbiting in an orbiting space station. External carotid artery supplies blood to the face and neck. Superficial muscles are the muscles closest to the skin surface and can usually be seen while a body is performing actions. The ascending aorta, arch of in the head and neck, blood circulates from the upper systemic loop, which originates at the aortic the major superficial veins of the arm include the cephalic and basilic veins, as well as the median cubital.
The brachiocephalic artery, the left common carotid artery, and the left subclavian artery. The vertebral artery is a major artery in the neck1. Olfactory (cn i), optic (cn ii), oculomotor. Brachiocephalic trunk, subclavian, common carotid, external carotid, internal carotid arteries veins: Discuss the formation of external and internal jugular veins.
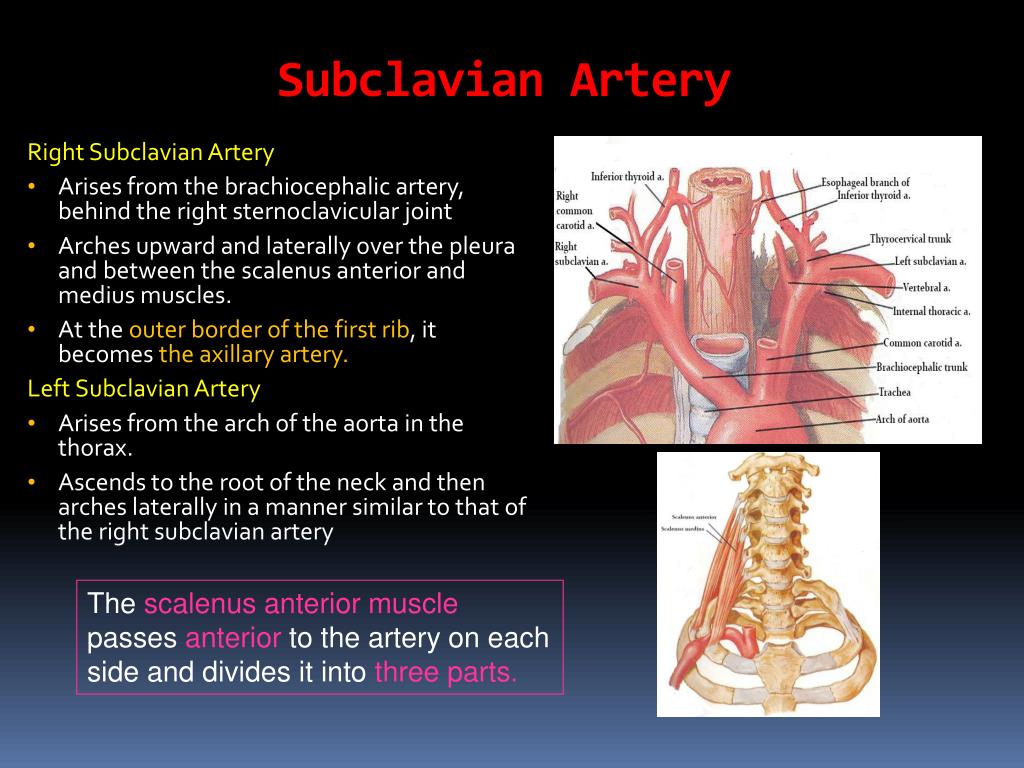
It branches from the subclavian artery, where it arises from the posterosuperior portion of the subclavian artery. The right and left subclavian arteries give rise to the thyrocervical trunk. Stylopharyngeus interval between the internal and external carotid ix nerve arteries in the upper part of the neck is occupied by the following structures. The latter is less invasive, but some research is… As with all regions of the body, your study should start out with a look at the living region being studied. The side of the neck presents a somewhat quadrilateral outline, limited, above, by the lower border of the body of the mandible. The external and internal jugular veins drain blood from the brain, head, and neck. Oxygenated blood enters the neck from the trunk through four major arteries:
The patient's age and the location, size, and duration of the mass are important pieces of information.
The major contents of carotid triangle are common carotid artery, internal carotid artery, external carotid artery, internal jugular vein and last 3 cranial the common carotid artery can be compressed against the notable anterior tubercle of transverse process of the 6th cervical vertebra termed carotid. Discuss the formation of external and internal jugular veins. Meningea media) and the inferior alveolar artery (a. A large artery that arises on each side of the neck, the common carotid artery is the primary source of oxygenated blood for the head and neck. left subclavian artery supplies blood 50. How well do you know the anatomy here? The first branch of the thyrocervical trunk is the inferior thyroid artery. It ascends though the foramina of the transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae, usually starting at c6 but entering as high as c42. Stylopharyngeus interval between the internal and external carotid ix nerve arteries in the upper part of the neck is occupied by the following structures. Internal jugular, external jugular, anterior jugular, subclavian and brachiocephalic veins nerves: The only major branches of the common carotid artery are its two terminating ones, which arise at the level of the fourth neck vertebra. As with all regions of the body, your study should start out with a look at the living region being studied. The carotid arteries are the major arteries of the head and neck.
The carotid system of arteries and the jugular system of veins. Brachiocephalic trunk right subclavian internal thoracic thyrocervical trunk vertebral right common carotid carotid sinus external carotid internal carotid. The external carotid artery is a major artery of the head and neck. The vertebral artery is a major artery in the neck1. Superficial muscles are the muscles closest to the skin surface and can usually be seen while a body is performing actions.
The external and internal jugular veins drain blood from the brain, head, and neck. Many in the neck help to stabilize or move the head. How well do you know the anatomy here? The patient's age and the location, size, and duration of the mass are important pieces of information. Yes the blood pressure in major arteries in the leg is greater than the blood pressure in arteries in neck during orbiting in an orbiting space station. It ascends though the foramina of the transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae, usually starting at c6 but entering as high as c42. The external carotid artery is a major artery of the head and neck. Review the major systemic arteries of the body including those of the neck, arm, forearm, abdomen, pelvis, thigh, and leg in this interactive tutorial.
Alveolaris on the neck of the branches of her not depart.
The side of the neck presents a somewhat quadrilateral outline, limited, above, by the lower border of the body of the mandible. From this trunk, several vessels arise, which go on to supply the neck. Just like other arteries in the body, neck arteries are also susceptible to blockages. The aorta is the largest artery in the body and is divided into 3 parts: The first branch of the thyrocervical trunk is the inferior thyroid artery. Olfactory (cn i), optic (cn ii), oculomotor. How are clogged arteries or arterial plaque treated? The carotid system of arteries and the jugular system of veins. A large artery that arises on each side of the neck, the common carotid artery is the primary source of oxygenated blood for the head and neck. The main arteries in the neck are the common carotids, and the main veins of the neck that return the blood from the head and face are the external rectus capitis posterior major (rectus capitis posticus major) arises by a pointed tendon from the spinous process of the axis, and, becoming broader as it. External carotid artery supplies blood to the face and neck. The common carotid artery of the neck. The latter is less invasive, but some research is…
The only major branches of the common carotid artery are its two terminating ones, which arise at the level of the fourth neck vertebra. The external carotid artery is a major artery of the head and neck. From the maxillary artery leaves several major branches: The main arteries in the neck are the common carotids, and the main veins of the neck that return the blood from the head and face are the external rectus capitis posterior major (rectus capitis posticus major) arises by a pointed tendon from the spinous process of the axis, and, becoming broader as it. Stylopharyngeus interval between the internal and external carotid ix nerve arteries in the upper part of the neck is occupied by the following structures.

A large artery that arises on each side of the neck, the common carotid artery is the primary source of oxygenated blood for the head and neck. Brachiocephalic trunk right subclavian internal thoracic thyrocervical trunk vertebral right common carotid carotid sinus external carotid internal carotid. Meningea media) and the inferior alveolar artery (a. The external and internal jugular veins drain blood from the brain, head, and neck. Three major arteries branch off the aortic arch: Internal carotid artery internal carotid arteries are major arteries of the head and neck that supply blood to the brain. A careful medical history should be obtained, and a thorough physical examination should be performed. Terms in this set (20).
Internal jugular, external jugular, anterior jugular, subclavian and brachiocephalic veins nerves:
However, neck arteries can work just as fine, even though they are the carotid arteries are major blood vessels in the neck that supply blood to the brain, neck, and face. The neck is supplied by arteries other than the carotids. Arteries are blood vessels that carry blood rich in oxygen in many instances, clogged arteries do not cause any symptoms until a major event, such as a heart clogged arteries in carotid artery disease may cause stroke precursors known as transient. The vertebral artery is a major artery in the neck1. Meningea media) and the inferior alveolar artery (a. Brachiocephalic trunk, subclavian, common carotid, external carotid, internal carotid arteries veins: There are arteries in the neck as shown in the image. Superficial muscles are the muscles closest to the skin surface and can usually be seen while a body is performing actions. Internal jugular, external jugular, anterior jugular, subclavian and brachiocephalic veins nerves: They're the major arteries that branch off from the common carotid arteries (they branch into internal and external carotids, both supplying oxygenated. External carotid artery supplies blood to the face and neck. The right and left subclavian arteries give rise to the thyrocervical trunk. The main arteries in the neck are the common carotids, and the main veins of the neck that return the blood from the head and face are the external rectus capitis posterior major (rectus capitis posticus major) arises by a pointed tendon from the spinous process of the axis, and, becoming broader as it.
There are two carotid arteries, one on the arteries in neck. The common carotid artery of the neck.


Posting Komentar
0 Komentar